Notice of changes to our Privacy Policy
An updated Privacy Policy was posted on the website of La Financière agricole and is effective April 25, 2025.
See the Notice of changes to the Privacy Policy for more information (in French only).
Crop Insurance
Make certain you meet the eligibility criteria for each product you wish to insure.
Contact an advisor at your service centre.
To facilitate the opening of your file, please fill out the following form:
| Insured crop | Enrolment deadline |
|---|---|
| Apiculture – Subgroup Bees | November 1 preceding the insurance year |
| Apiculture – Subgroup Honey | April 30 |
| Apple Trees - Plan A | December 1 preceding the insurance year |
| Apples - Plan B | April 1 of the insurance year |
| Autumn Cereals | November 1 preceding the insurance year |
| Cereal, Grain Corn and High-Protein Oilseed Crops – Grain | April 30 |
| Cereal, Grain Corn and High-Protein Oilseed Crops – Seed | April 30 |
| Cranberries | April 30 |
| Day-Neutral Strawberries | April 30 |
| Grain Corn – Collective | April 30 |
| Haskap berries | September 30 preceding the insurance year |
| Hay, Corn Silage, Cereals and Emerging crops | April 30 |
| Maple syrup | February 15 of the insurance year |
| Market Garden Crops | April 30, except for vegetables grown for processing insurable until the seeding or planting start date indicated in the Directory of the dates for applying to the Crop Insurance Program |
| Market Garden Crops – Local Market Gardening | April 30 |
| Market Garden Crops – Perennial Vegetables | According to coverage chosen |
| Potatoes | April 30 |
| Semi-cultivated low-bush blueberries | December 1 preceding the insurance year |
| Strawberries and Raspberries - Fall and Spring Enrolment | April 30 for spring enrolment November 15 preceding the insurance year for fall enrolment |
| Vegetables Grown for Processing | Before seeding or by the seeding cut-off date for each crop, i.e. July 15 for beans and June 24 for sweet corn and green peas |
The premium is usually cost-shared by the Canadian and Québec governments (60%) and participants (40%), although these proportions may vary according to the crops and benefit options chosen.
At the time of enrolment, you must choose from the coverage options that are available for your crops and that best suit your situation.
The coverage option corresponds to the level of coverage you want to be insured for. It reflects the part of the damage covered by the insurance and is expressed in terms of a percentage. Coverage options vary according to the crop. The most common are between 60% and 80%.
The insurable value represents the monetary value of the insured crop. It varies according to the units insured and the unit price. To determine the insurable value, multiply the number of insured units by the selected unit price:
Insurable Value = Number of Insured Units x Unit Price
The insured value is determined by multiplying the insurable value by the coverage option chosen by the participant:
Insured Value = Coverage Option x Insurable Value
The insured value represents the maximum amount that the participant could receive as compensation depending on the circumstances of the claim.
Unlike a home or auto deductible, the ASREC deductible is not expressed as a fixed amount, but rather as a percentage of the insurable value. The basic rating methodology is established for each coverage option offered. In addition, individual risks are taken into account through the loss ratio and years of experience.
The deductible is the portion of the loss that is the responsibility of the insured (not compensated by the insurer; in the case of ASREC, the insurer is the FADQ). The deductible varies according to the crops and the coverage options chosen. It is expressed as a percentage and corresponds to 100% minus the level of coverage (coverage option) chosen.
Thus, the higher the deductible, the greater the share of the risk assumed by the insured. On the other hand, the insurance premium decreases as the deductible increases. Losses below the deductible percentage are the responsibility of the client. The deductible has a direct impact on the insured value and therefore on the possible compensation.
The deductible is the difference between the insurable value and the insured value:
Deductible = Insurable Value - Insured Value
The minimum deductible that can be offered is defined in the legal framework:
Example of the impact of the deductible on compensation:
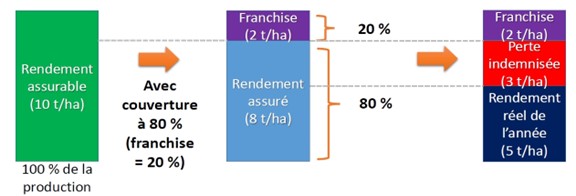
Insurable production> With 80% coverage (20% deductible)
Deductible (2t/ha) Insured production (8t/ha)> 20% 80%>
Deductible (2t/ha) Compensated loss (3t/ha) Actual production for year ((5t/ha)